What is an Event Recorder?
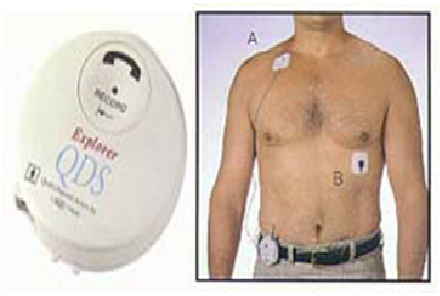
An Event Recorder is a recording device used to record the heart rhythm. It is similar to an EKG. You can wear the recorder over a period of 14 days to 30 days, while you go about your usual daily activities. When you feel symptoms, you press a record button and the event monitor records and stores up to five events of your heart’s electrical activity. The Event Recorder is about the size of a pager. You can clip it to a belt, your pants, or place it in your pocket. Two electrodes (sticky patches) are worn on your chest. A wire attaches the electrodes to the Event Recorder. The Event Recorder is worn day and night, and continuously scans your heart’s electrical activity.
An Event Recorder is a recording device used to record the heart rhythm. It is similar to an EKG. You can wear the recorder over a period of 14 days to 30 days, while you go about your usual daily activities. When you feel symptoms, you press a record button and the event monitor records and stores up to five events of your heart’s electrical activity. The Event Recorder is about the size of a pager. You can clip it to a belt, your pants, or place it in your pocket. Two electrodes (sticky patches) are worn on your chest. A wire attaches the electrodes to the Event Recorder. The Event Recorder is worn day and night, and continuously scans your heart’s electrical activity.
How do I prepare for the procedure?
There is no special preparation for event monitoring. You may eat and go about your normal activities, unless you are told otherwise. Make sure you wear a two-piece outfit to make the Event Recorder easier to hook up.
What is an Event Recorder used for?
If you have been having recurrent symptoms, such as dizziness, chest pain, palpitation, or fainting spells, the doctor will use an Event Recorder to help determine if these symptoms are caused by an arrhythmia.
During an arrhythmia (abnormal heart rhythm), the heart will either beat too fast, too slow, or irregularly. Doctors can diagnose an arrhythmia by obtaining an EKG, a recording of the heart’s electrical activity. Quite often, an arrhythmia will not occur in a brief period of actual recording like when you are getting an EKG at your doctor’s office. If your doctor suspects you have an arrhythmia, he or she will want to record the EKG when you are having symptoms.
If your symptoms are infrequent, you may require the use of an Event Recorder to catch your EKG during your symptoms.
How long does this test take?
Instructions and set up take about 15 to 30 minutes to complete.
There is no special preparation for event monitoring. You may eat and go about your normal activities, unless you are told otherwise. Make sure you wear a two-piece outfit to make the Event Recorder easier to hook up.
What is an Event Recorder used for?
If you have been having recurrent symptoms, such as dizziness, chest pain, palpitation, or fainting spells, the doctor will use an Event Recorder to help determine if these symptoms are caused by an arrhythmia.
During an arrhythmia (abnormal heart rhythm), the heart will either beat too fast, too slow, or irregularly. Doctors can diagnose an arrhythmia by obtaining an EKG, a recording of the heart’s electrical activity. Quite often, an arrhythmia will not occur in a brief period of actual recording like when you are getting an EKG at your doctor’s office. If your doctor suspects you have an arrhythmia, he or she will want to record the EKG when you are having symptoms.
If your symptoms are infrequent, you may require the use of an Event Recorder to catch your EKG during your symptoms.
How long does this test take?
Instructions and set up take about 15 to 30 minutes to complete.
Cardiac Specialty Care
• Structural Heart Disease
• TAVR
• CardioMEMS (Heart Failure)
• PFO Closure
• TAVR
• CardioMEMS (Heart Failure)
• PFO Closure
• Coronary Intervention
• Complex Higher-Risk (And Indicated) Patients (CHIP) Angioplasty
• Atherectomy
• Impella and ECMO Support
• Complex Higher-Risk (And Indicated) Patients (CHIP) Angioplasty
• Atherectomy
• Impella and ECMO Support
• Peripheral Angioplasty
• Varicose Vein Treatment (Venous Ablation)
• DVT thrombectomy - IVC filter
• Carotid Stenting
• Varicose Vein Treatment (Venous Ablation)
• DVT thrombectomy - IVC filter
• Carotid Stenting
• Rhythm Management
• Pacemaker
• Holter Monitoring
• Exercise Stress Test
• Echocardiography
• Nuclear Stress Test
• Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP)
• Pacemaker
• Holter Monitoring
• Exercise Stress Test
• Echocardiography
• Nuclear Stress Test
• Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP)
