For patients who are unable to exercise, a medication called Dobutamine will be used to make your heart beat harder and faster as if you were exercising. This will be combined with a nuclear imaging material that is injected into the bloodstream and enables the Nuclear Medicine Technologist to take images/pictures of your heart. These images/pictures will help to determine if there is an area of your heart muscle that is not receiving enough blood due to narrowed or diseased arteries in your heart. The nuclear imaging material is not a “dye.” It is used routinely and has been shown to be safe.
What will the pictures show?
The nuclear material travels through the bloodstream (arteries) to the “target” organ, the heart muscle. The nuclear imaging material gives off a small amount of radiation that can be seen with a special camera. Areas of the heart muscle with reduced blood flow because of blocked or narrowed arteries will not contain as much nuclear material as those with healthy arteries and normal blood flow. Areas of decreased blood flow are called “defects.” The Cardiologist will analyze these pictures.
How is it done?
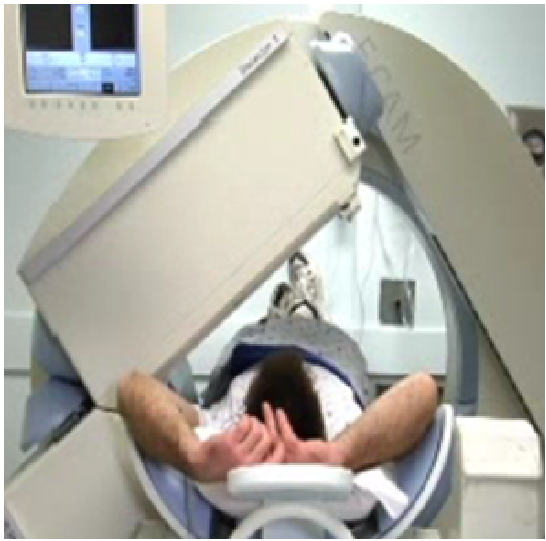
The test is done in two parts, resting and stress. The first part is done after an intravenous (IV) is started in your arm and the nuclear imaging material is injected into your vein. This will be allowed to circulate for 30 minutes while you rest comfortably on a bed or in a chair. Following this circulation time, the first scan will be done. This scan takes about 15 minutes. It is important that you lie still with your left arm above your head for each scan, while the camera rotates around your chest. Shortly after completing this scan, the second part of the test will begin.
What will the pictures show?
The nuclear material travels through the bloodstream (arteries) to the “target” organ, the heart muscle. The nuclear imaging material gives off a small amount of radiation that can be seen with a special camera. Areas of the heart muscle with reduced blood flow because of blocked or narrowed arteries will not contain as much nuclear material as those with healthy arteries and normal blood flow. Areas of decreased blood flow are called “defects.” The Cardiologist will analyze these pictures.
How is it done?
The test is done in two parts, resting and stress. The first part is done after an intravenous (IV) is started in your arm and the nuclear imaging material is injected into your vein. This will be allowed to circulate for 30 minutes while you rest comfortably on a bed or in a chair. Following this circulation time, the first scan will be done. This scan takes about 15 minutes. It is important that you lie still with your left arm above your head for each scan, while the camera rotates around your chest. Shortly after completing this scan, the second part of the test will begin.
DO NOT EAT OR DRINK between the two parts of the test.
Before the second part of the test begins, you will be placed on a bed or stretcher and have several electrodes (small sticky patches) placed on your chest. While resting on the bed, the medication Dobutamine is slowly dripped through the intravenous (IV) for about 15 to 20 minutes. A cardiologist (heart physician) will be with you for this part of the test. Normally, the heart muscle will squeeze faster and harder while receiving the Dobutamine. When your heart has reached a certain rate and/or when the physician has obtained enough information, the nuclear imaging material will be injected again and the Dobutamine will be stopped. If your heart rate does not increase enough with the Dobutamine, you may be asked to do moderate leg or arm exercises. You will be asked to tell the physician if you experience any chest pain or shortness of breath. Once again, the nuclear material will be allowed to circulate for 30 minutes while you rest and then the final scan will be done under the same camera. You will be allowed to eat and drink during this waiting period. This scan takes about 15 minutes. The two scans will help to determine if any defects or blockages are temporary, or if they are permanent as a result of earlier heart damage.
How do I prepare?
1. Bring all of your signed doctors orders and referrals with you.
2. Bring a list of your medications with you.
3.Do not eat or drink anything after midnight the night before.
*Especially no CAFFEINE and no TOBACCO the day of the test.
4. CONSULT THE PHYSICIAN who ordered the test about your medications. Get specific instructions about Beta Blockers and medications for diabetes.
5. Wear comfortable clothing. You will be wearing a hospital gown for the test.
How long does it take?
Allow 3-1/2 to 4 hours for the test.
Before the second part of the test begins, you will be placed on a bed or stretcher and have several electrodes (small sticky patches) placed on your chest. While resting on the bed, the medication Dobutamine is slowly dripped through the intravenous (IV) for about 15 to 20 minutes. A cardiologist (heart physician) will be with you for this part of the test. Normally, the heart muscle will squeeze faster and harder while receiving the Dobutamine. When your heart has reached a certain rate and/or when the physician has obtained enough information, the nuclear imaging material will be injected again and the Dobutamine will be stopped. If your heart rate does not increase enough with the Dobutamine, you may be asked to do moderate leg or arm exercises. You will be asked to tell the physician if you experience any chest pain or shortness of breath. Once again, the nuclear material will be allowed to circulate for 30 minutes while you rest and then the final scan will be done under the same camera. You will be allowed to eat and drink during this waiting period. This scan takes about 15 minutes. The two scans will help to determine if any defects or blockages are temporary, or if they are permanent as a result of earlier heart damage.
How do I prepare?
1. Bring all of your signed doctors orders and referrals with you.
2. Bring a list of your medications with you.
3.Do not eat or drink anything after midnight the night before.
*Especially no CAFFEINE and no TOBACCO the day of the test.
4. CONSULT THE PHYSICIAN who ordered the test about your medications. Get specific instructions about Beta Blockers and medications for diabetes.
5. Wear comfortable clothing. You will be wearing a hospital gown for the test.
How long does it take?
Allow 3-1/2 to 4 hours for the test.
Cardiac Specialty Care
• Structural Heart Disease
• TAVR
• CardioMEMS (Heart Failure)
• PFO Closure
• TAVR
• CardioMEMS (Heart Failure)
• PFO Closure
• Coronary Intervention
• Complex Higher-Risk (And Indicated) Patients (CHIP) Angioplasty
• Atherectomy
• Impella and ECMO Support
• Complex Higher-Risk (And Indicated) Patients (CHIP) Angioplasty
• Atherectomy
• Impella and ECMO Support
• Peripheral Angioplasty
• Varicose Vein Treatment (Venous Ablation)
• DVT thrombectomy - IVC filter
• Carotid Stenting
• Varicose Vein Treatment (Venous Ablation)
• DVT thrombectomy - IVC filter
• Carotid Stenting
• Rhythm Management
• Pacemaker
• Holter Monitoring
• Exercise Stress Test
• Echocardiography
• Nuclear Stress Test
• Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP)
• Pacemaker
• Holter Monitoring
• Exercise Stress Test
• Echocardiography
• Nuclear Stress Test
• Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP)
