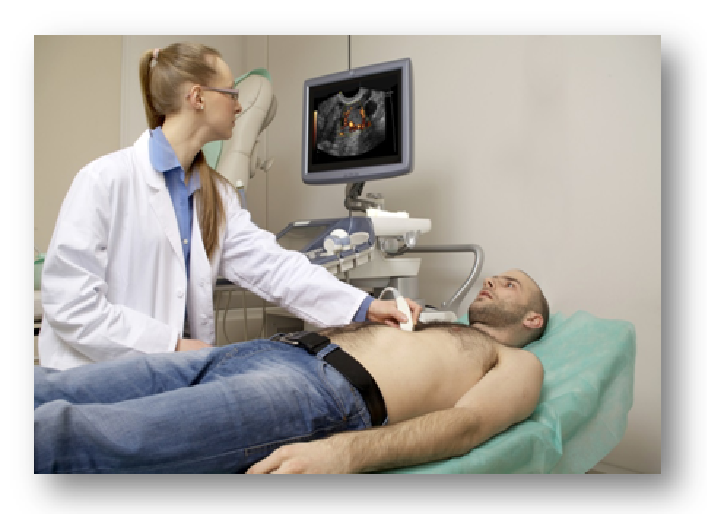
An echocardiogram is a noninvasive (the skin is not pierced) procedure used to assess the heart’s function and structures. During the procedure, a transducer (like a microphone) sends out ultrasonic sound waves at a frequency too high to be heard. When the transducer is placed on the chest at certain locations and angles, the ultrasonic sound waves move through the skin and other body tissues to the heart tissues, where the waves bounce or “echo” off of the heart structures. These sound waves are sent to a computer that can create moving images of the heart walls and valves.
An echocardiogram may utilize several special types of echocardiography, as listed below:
• M-mode echocardiography. This, the simplest type of echocardiography, produces an image that is similar to a tracing rather than an actual picture of heart structures. M-mode echo is useful for measuring heart structures, such as the heart’s pumping chambers, the size of the heart itself, and the thickness of the heart walls.
• Doppler echocardiography. This Doppler technique is used to measure and assess the flow of blood through the heart’s chambers and valves. The amount of blood pumped out with each beat is an indication of the heart’s functioning. Also, Doppler can detect abnormal blood flow within the heart, which can indicate a problem with one or more of the heart’s four valves, or with the heart’s walls.
• Color Doppler. Color Doppler is an enhanced form of Doppler echocardiography. With color Doppler, different colors are used to designate the direction of blood flow. This simplifies the interpretation of the Doppler technique.
• 2-D (two-dimensional) echocardiography. This technique is used to “see” the actual motion of the heart structures. A 2-D echo view appears cone-shaped on the monitor, and the real-time motion of the heart’s structures can be observed. This enables the doctor to see the various heart structures at work and evaluate them.
• 3-D (three-dimensional) echocardiography. 3-D echo technique captures three-dimensional views of the heart structures with greater depth than 2-D echo. The live or “real time” images allow for a more accurate assessment of heart function by using measurements taken while the heart is beating. 3-D echo shows enhanced views of the heart’s anatomy and can be used to determine the appropriate plan of treatment for a person with heart disease.
An echocardiogram may utilize several special types of echocardiography, as listed below:
• M-mode echocardiography. This, the simplest type of echocardiography, produces an image that is similar to a tracing rather than an actual picture of heart structures. M-mode echo is useful for measuring heart structures, such as the heart’s pumping chambers, the size of the heart itself, and the thickness of the heart walls.
• Doppler echocardiography. This Doppler technique is used to measure and assess the flow of blood through the heart’s chambers and valves. The amount of blood pumped out with each beat is an indication of the heart’s functioning. Also, Doppler can detect abnormal blood flow within the heart, which can indicate a problem with one or more of the heart’s four valves, or with the heart’s walls.
• Color Doppler. Color Doppler is an enhanced form of Doppler echocardiography. With color Doppler, different colors are used to designate the direction of blood flow. This simplifies the interpretation of the Doppler technique.
• 2-D (two-dimensional) echocardiography. This technique is used to “see” the actual motion of the heart structures. A 2-D echo view appears cone-shaped on the monitor, and the real-time motion of the heart’s structures can be observed. This enables the doctor to see the various heart structures at work and evaluate them.
• 3-D (three-dimensional) echocardiography. 3-D echo technique captures three-dimensional views of the heart structures with greater depth than 2-D echo. The live or “real time” images allow for a more accurate assessment of heart function by using measurements taken while the heart is beating. 3-D echo shows enhanced views of the heart’s anatomy and can be used to determine the appropriate plan of treatment for a person with heart disease.
Reasons for the procedure
An echocardiogram may be performed for further evaluation of signs or symptoms that may suggest:
• Atherosclerosis. A gradual clogging of the arteries over many years by fatty materials and other substances in the blood stream that can lead to abnormalities in the wall motion or pumping function of your heart.
• Cardiomyopathy. An enlargement of the heart due to thickening or weakening of the heart muscle
• Congenital heart disease. Defects in one or more heart structures that occur during formation of the fetus, such as a ventricular septal defect (hole in the wall between the two lower chambers of the heart).
• Congestive heart failure. A condition in which the heart muscle has become weakened to an extent that blood cannot be pumped efficiently, causing fluid buildup (congestion) in the blood vessels and lungs, and edema (swelling) in the feet, ankles, and other parts of the body.
• Aneurysm. A dilation of a part of the heart muscle or the aorta (the large artery that carries oxygenated blood out of the heart to the rest of the body), which may cause weakness of the tissue at the site of the aneurysm.
An echocardiogram may be performed for further evaluation of signs or symptoms that may suggest:
• Atherosclerosis. A gradual clogging of the arteries over many years by fatty materials and other substances in the blood stream that can lead to abnormalities in the wall motion or pumping function of your heart.
• Cardiomyopathy. An enlargement of the heart due to thickening or weakening of the heart muscle
• Congenital heart disease. Defects in one or more heart structures that occur during formation of the fetus, such as a ventricular septal defect (hole in the wall between the two lower chambers of the heart).
• Congestive heart failure. A condition in which the heart muscle has become weakened to an extent that blood cannot be pumped efficiently, causing fluid buildup (congestion) in the blood vessels and lungs, and edema (swelling) in the feet, ankles, and other parts of the body.
• Aneurysm. A dilation of a part of the heart muscle or the aorta (the large artery that carries oxygenated blood out of the heart to the rest of the body), which may cause weakness of the tissue at the site of the aneurysm.
• Valvular heart disease. Malfunction of one or more of the heart valves that may cause an abnormality of the blood flow within the heart.
• Cardiac tumor. A tumor of the heart that may occur on the outside surface of the heart, within one or more chambers of the heart (intracavitary), or within the muscle tissue (myocardium) of the heart.
• Pericarditis. An inflammation or infection of the sac that surrounds the heart.
An echocardiogram may also be simply performed to assess the heart’s overall function and general structure.
There may be other reasons for your doctor to recommend an echocardiogram.
Risks of the procedure
For some patients, having to lie still on the examination table for the length of the procedure may cause some discomfort or pain.
There may be other risks depending on your specific medical condition. Be sure to discuss any concerns with your doctor prior to the procedure.
Before the procedure
• Your doctor will explain the procedure to you and offer you the opportunity to ask any questions that you might have about the procedure.
• Generally, no prior preparation, such as fasting or sedation, is required.
• Notify your doctor of all medications (prescription and over-the-counter) and herbal supplements that you are taking.
• Notify your doctor if you have a pacemaker.
• Based on your medical condition, your doctor may request other specific preparation.
During the procedure
An echocardiogram may be performed on an outpatient basis or as part of your stay in a hospital. Procedures may vary depending on your condition and your doctor’s practices.
Generally, an echocardiogram follows this process:
• You will be asked to remove any jewelry or other objects that may interfere with the procedure. You may wear your glasses, dentures, or hearing aids if you use any of these.
• You will be asked to remove clothing from the waist up and will be given a gown to wear.
• You will lie on a table or bed, positioned on your left side. A pillow or wedge may be placed behind your back for support.
• You will be connected to an ECG monitor that records the electrical activity of the heart and monitors the heart during the procedure using small, adhesive electrodes. The ECG tracings that record the electrical activity of the heart will be compared to the images displayed on the echocardiogram monitor.
• The room will be darkened so that the images on the echo monitor can be viewed by the technologist.
• The technologist will place warmed gel on your chest and then place the transducer probe on the gel. You will feel a slight pressure as the technologist positions the transducer to obtain the desired images of your heart.
• During the test, the technologist will move the transducer probe around and apply varying amounts of pressure to obtain images of different locations and structures of your heart. The amount of pressure behind the probe should not be uncomfortable. If it does make you uncomfortable, however, let the technologist know.
• After the procedure has been completed, the technologist will wipe the gel from your chest and remove the ECG electrode pads. You may then put on your clothes.
After the procedure
You may resume your usual diet and activities unless your doctor advises you differently.
Generally, there is no special type of care following an echocardiogram. However, your doctor may give you additional or alternate instructions after the procedure, depending on your particular situation.
• Cardiac tumor. A tumor of the heart that may occur on the outside surface of the heart, within one or more chambers of the heart (intracavitary), or within the muscle tissue (myocardium) of the heart.
• Pericarditis. An inflammation or infection of the sac that surrounds the heart.
An echocardiogram may also be simply performed to assess the heart’s overall function and general structure.
There may be other reasons for your doctor to recommend an echocardiogram.
Risks of the procedure
For some patients, having to lie still on the examination table for the length of the procedure may cause some discomfort or pain.
There may be other risks depending on your specific medical condition. Be sure to discuss any concerns with your doctor prior to the procedure.
Before the procedure
• Your doctor will explain the procedure to you and offer you the opportunity to ask any questions that you might have about the procedure.
• Generally, no prior preparation, such as fasting or sedation, is required.
• Notify your doctor of all medications (prescription and over-the-counter) and herbal supplements that you are taking.
• Notify your doctor if you have a pacemaker.
• Based on your medical condition, your doctor may request other specific preparation.
During the procedure
An echocardiogram may be performed on an outpatient basis or as part of your stay in a hospital. Procedures may vary depending on your condition and your doctor’s practices.
Generally, an echocardiogram follows this process:
• You will be asked to remove any jewelry or other objects that may interfere with the procedure. You may wear your glasses, dentures, or hearing aids if you use any of these.
• You will be asked to remove clothing from the waist up and will be given a gown to wear.
• You will lie on a table or bed, positioned on your left side. A pillow or wedge may be placed behind your back for support.
• You will be connected to an ECG monitor that records the electrical activity of the heart and monitors the heart during the procedure using small, adhesive electrodes. The ECG tracings that record the electrical activity of the heart will be compared to the images displayed on the echocardiogram monitor.
• The room will be darkened so that the images on the echo monitor can be viewed by the technologist.
• The technologist will place warmed gel on your chest and then place the transducer probe on the gel. You will feel a slight pressure as the technologist positions the transducer to obtain the desired images of your heart.
• During the test, the technologist will move the transducer probe around and apply varying amounts of pressure to obtain images of different locations and structures of your heart. The amount of pressure behind the probe should not be uncomfortable. If it does make you uncomfortable, however, let the technologist know.
• After the procedure has been completed, the technologist will wipe the gel from your chest and remove the ECG electrode pads. You may then put on your clothes.
After the procedure
You may resume your usual diet and activities unless your doctor advises you differently.
Generally, there is no special type of care following an echocardiogram. However, your doctor may give you additional or alternate instructions after the procedure, depending on your particular situation.
Cardiac Specialty Care
• Structural Heart Disease
• TAVR
• CardioMEMS (Heart Failure)
• PFO Closure
• TAVR
• CardioMEMS (Heart Failure)
• PFO Closure
• Coronary Intervention
• Complex Higher-Risk (And Indicated) Patients (CHIP) Angioplasty
• Atherectomy
• Impella and ECMO Support
• Complex Higher-Risk (And Indicated) Patients (CHIP) Angioplasty
• Atherectomy
• Impella and ECMO Support
• Peripheral Angioplasty
• Varicose Vein Treatment (Venous Ablation)
• DVT thrombectomy - IVC filter
• Carotid Stenting
• Varicose Vein Treatment (Venous Ablation)
• DVT thrombectomy - IVC filter
• Carotid Stenting
• Rhythm Management
• Pacemaker
• Holter Monitoring
• Exercise Stress Test
• Echocardiography
• Nuclear Stress Test
• Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP)
• Pacemaker
• Holter Monitoring
• Exercise Stress Test
• Echocardiography
• Nuclear Stress Test
• Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP)
