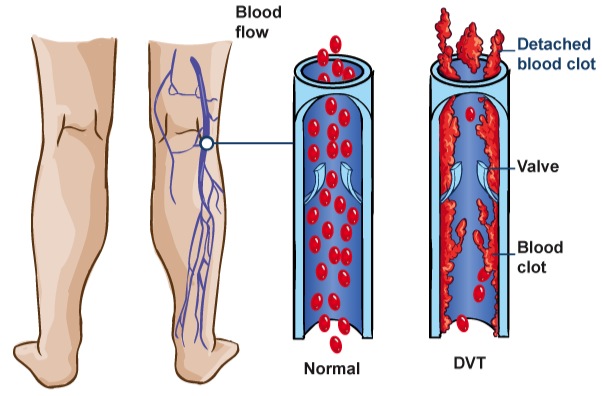
DVT is the formation of a clot (thrombus) in a deep vein, most commonly:
- In the lower limb: femoral, popliteal, or tibial veins
- Sometimes in the pelvis or upper limbs (less common)
?? 2. Why is it Dangerous?
The biggest risk is that the clot can dislodge and travel through the venous system to the lungs, causing a Pulmonary Embolism (PE) — a life-threatening condition.
???? 3. Pathophysiology: Why Does DVT Happen?
DVT is typically due to Virchow’s Triad — the three primary risk factors that promote clot formation:
???? Virchow's Triad:
???? 4. Signs and Symptoms
Not all patients with DVT have symptoms, but common signs include:
- Swelling (usually unilateral)
- Pain or tenderness (often in the calf or thigh)
- Redness or warmth over the vein
- Dilated superficial veins
- Homan’s sign: calf pain on dorsiflexion of the foot (not reliable diagnostically)
If the clot embolizes: sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, tachycardia — signs of pulmonary embolism.
???? 5. Diagnosis
- D-dimer test: Elevated in DVT but nonspecific (also rises in inflammation, cancer, post-surgery)
- Compression Ultrasound: First-line imaging test
- Venography (rarely used now)
- CT/MRI venography: if clot is suspected in pelvis or upper leg
???? 6. Risk Factors
Modifiable:
- Immobility (long travel, bed rest)
- Surgery (especially orthopedic)
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Oral contraceptives/Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
Non-modifiable:
- Age
- Personal or family history of DVT/PE
- Inherited clotting disorders (e.g., Protein C/S deficiency, Factor V Leiden)
- Pregnancy/postpartum
- Cancer
???? 7. Treatment
???? A. Anticoagulation (Mainstay of treatment)
- Heparin (LMWH or unfractionated)
- Warfarin (long-term, needs INR monitoring)
- DOACs (Direct Oral Anticoagulants): apixaban, rivaroxaban, dabigatran
???? B. Thrombolysis
- For severe cases or massive PE
- Involves clot-dissolving medications like tPA
???? C. IVC Filter
- Inferior vena cava filter can be placed to prevent clots from reaching the lungs
- Reserved for patients who can’t take anticoagulants
???? 8. Prevention (Especially in High-Risk Patients)
- Early ambulation after surgery
- Compression stockings
- Intermittent pneumatic compression devices
- Prophylactic anticoagulation (e.g., in hospitalized patients)

